Connecting to GitHub with SSH

With SSH keys, you can connect to GitHub without supplying your email and password every time you push.
When you set up SSH, you will need to generate a new SSH key and add it to the ssh-agent. You must add the SSH key to your account on GitHub before you use the key to authenticate.
Checking for existing SSH keys
Before you generate an SSH key, you can check to see if you have any existing SSH keys.
Go to the terminal and type:
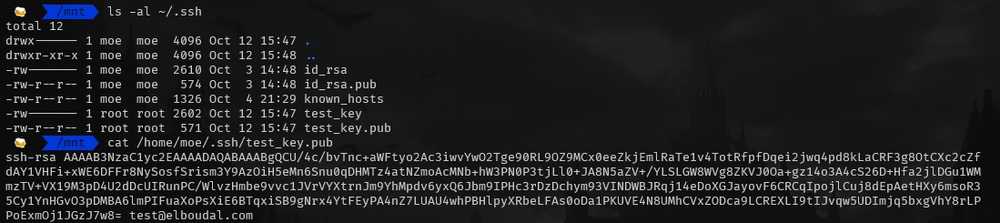
ls -al ~/.sshIt will list down all the ssh keys on your system:

By default, the file names of the public keys are one of the following:
- id_dsa.pub
- id_ecdsa.pub
- id_ed25519.pub
- id_rsa.pub
If the key does not exist, you will have to create a new one.
Generate the key if it doesn't exist
To generate a new key, you should go to the terminal and type:
ssh-keygen -trsa -C your-github-emailIf you need root privileges you can type:
sudo ssh-keygen -trsa -C your-github-email

Enter fil in which to save the key or click enter to accept the default file.

Enter the passphrase or click enter to leave it empty.

Repeat the same passphrase you entered in the previous step.
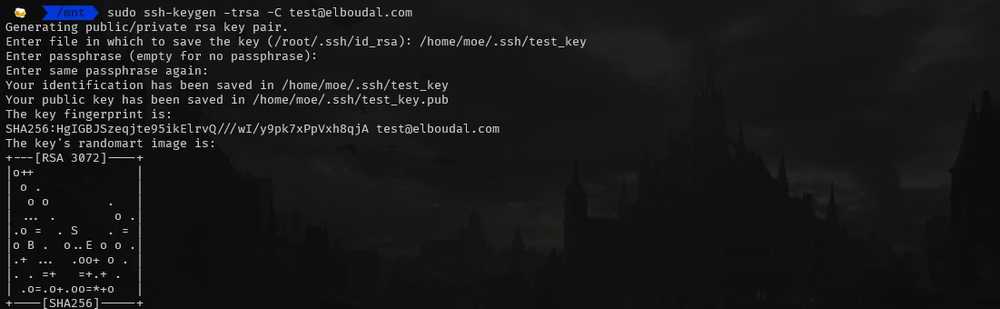
You have successfully created an ssh key.
Copy the public ssh key content
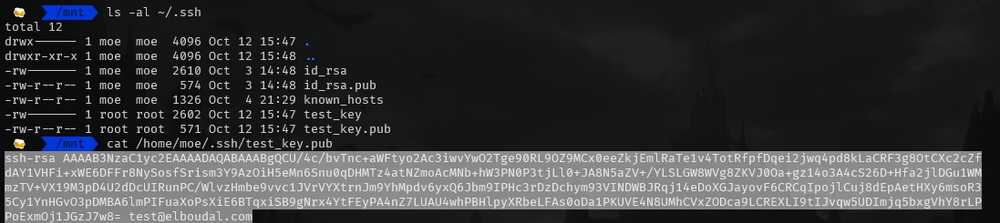
To display the ssh key content go to the terminal and type:
cat /home/moe/.ssh/test_key.pub
Select and copy the content:
Add new ssh key to github
Go to Github > settings > SSH and GPG keys or click here.
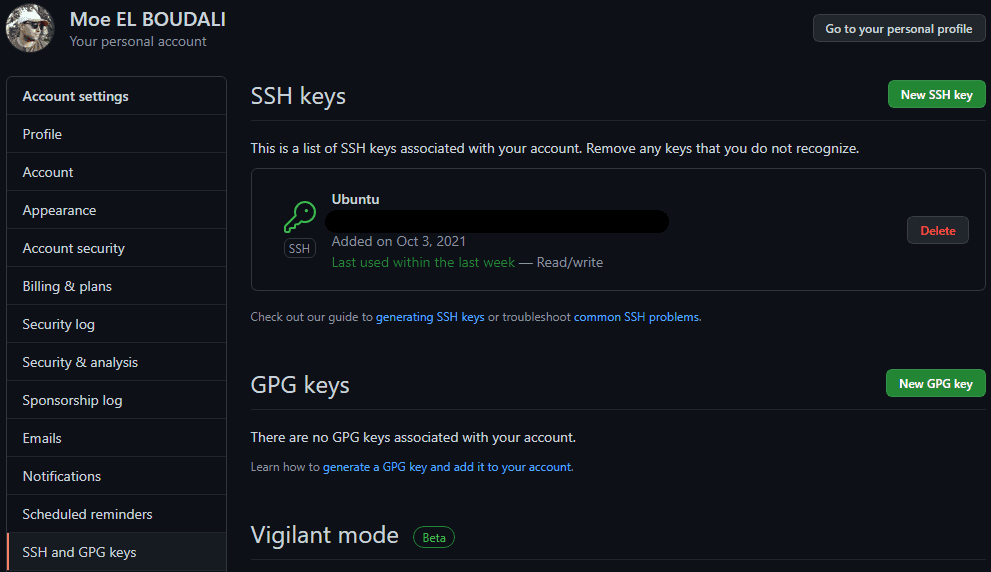
Click New SSH key button.
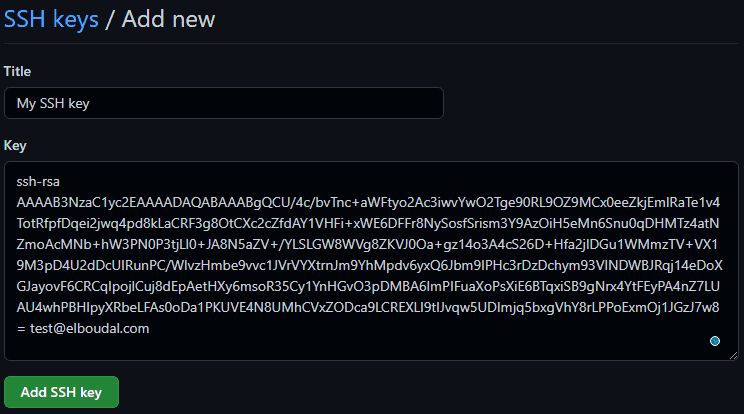
Add Title, paste the key content, click Add SSH key, and Confirm access with your GitHub password.
That's it!
Now You can connect to GitHub without supplying your username and personal access token at each visit.
NB: If you haven't used your SSH key for a year, then GitHub will automatically delete your inactive SSH key as a security precaution.